Products Are Broken Down Using Beta Oxidation Which Occurs
ATP can be used by cells to drive endergonic reactions. -Cholesterol used for steroid hormone synthesis.
Oxidation Of Fatty Acids Ketogenesis Basicmedical Key
Beta-oxidation is fueled by free fatty acids.
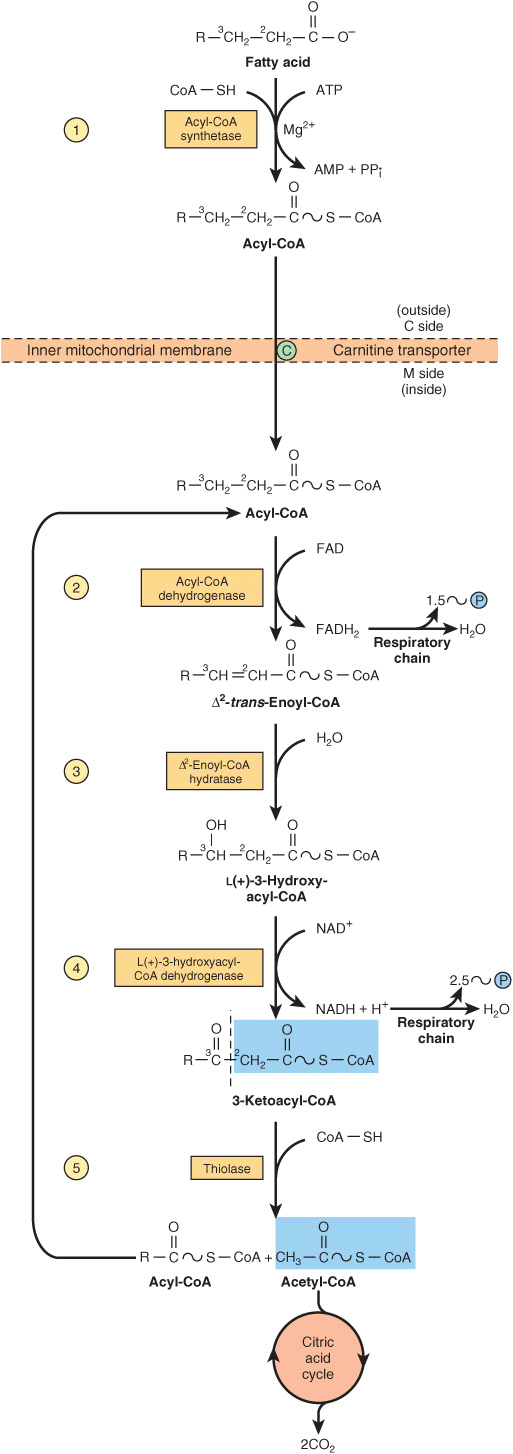
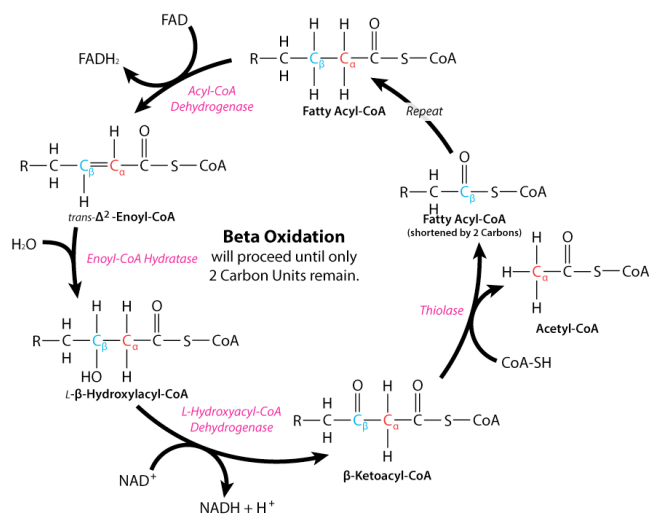
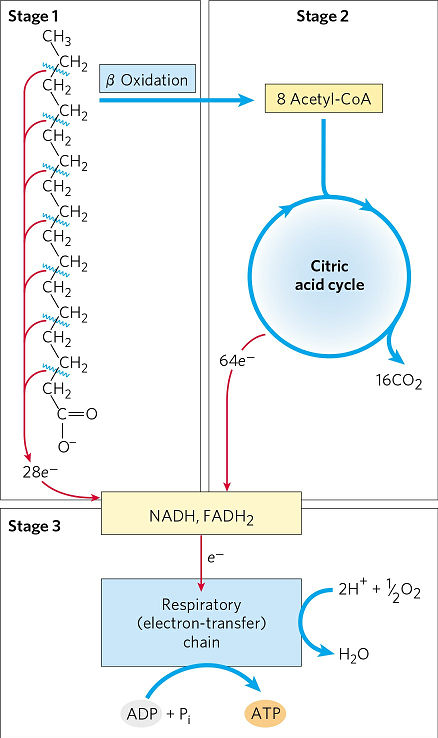
. The final stage is characterized by the release of energy by reducing NAD and NADH. Beta oxidation also produces acetyl CoA that enters the TCA cycle by combining with oxaloacetate to form citric acid. The total process undergoes in three major steps.
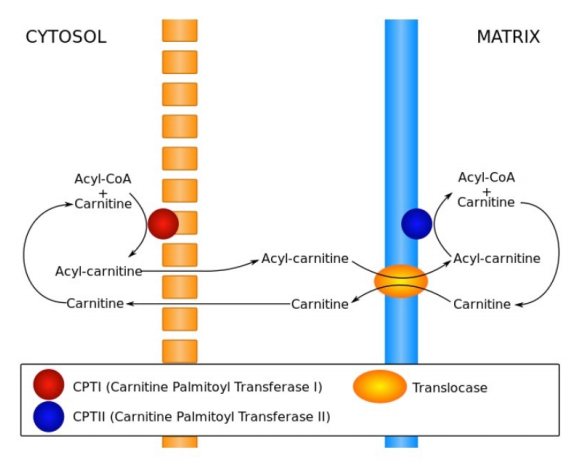
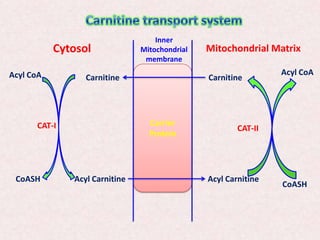
In particular beta-oxidation occurs when long fatty acids that are converted to acyl-CoA chains are broken down into increasingly shorter chains. Beta-oxidation of fatty acids occurs in the mitochondrial matrix so the fatty acid substrate in the form of fatty acyl-CoA must be transported across the outer and inner membranes of mitochondria that are impervious to fatty acids or fatty acids. Glycerol enters the glycolytic pathways and can be used to make a pyruvate.
Fatty acids enter the mitochondria and are used to generate Acetyl CoA that can be used in the citric acid cycle. -Absorbed as fatty acids monoglycerides and cholesterol. This process provides energy from fats.
What is the net number of ATP generated directly during glycolysis per molecule of glucose. Beta Oxidation Definition. The de novo biosynthesis explain beta oxidation of palmitic acid sphingolipids starts with palmitoyl-CoA to generate 3-ketodihydrosphingosine which yields H2O2 from complete of.
In biochemistry and metabolism beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA which enters the citric acid cycle and NADH and FADH2 which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport. A Prior to proper beta-oxidation the fatty acid is activated for energy production. The products of beta-oxidation are.
The products of beta-oxidation can be broken up into two groups. Beta-oxidation is the process by which long chain fatty acyl CoA is degraded. What is the beta oxidation of palmitic acid.
BETA OXIDATION AND LIPID METABOLISM. -In the fasted-state beta-oxidation occurs to provide intermediates for the citric acid cycle. FADH2 NADH and H fall into.
In biochemistry and metabolism beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA which enters the citric acid cycle and NADH and FADH 2 which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport. A further metabolic process the citric acid cycle or the Krebs cycle produces ATP as a by-product of this reaction which. It is named as such because the beta carbon of.
The process of beta oxidation occurs to release acetyl-CoA to be used in the citric acid cycle. In the process of beta-oxidation fatty acid molecules are broken down into energy through multiple steps. More specifically beta oxidation consists in breaking down long fatty acids that have been converted to acyl-CoA chains into progressively smaller fatty acyl-CoA chains.
During lipid catabolism or lipolysis triglycerides are broken down into a glycerol and 3 fatty acids. ADP is converted into ATP by the addition of a phosphate group. When substrate-level phosphorylation occurs it means that.
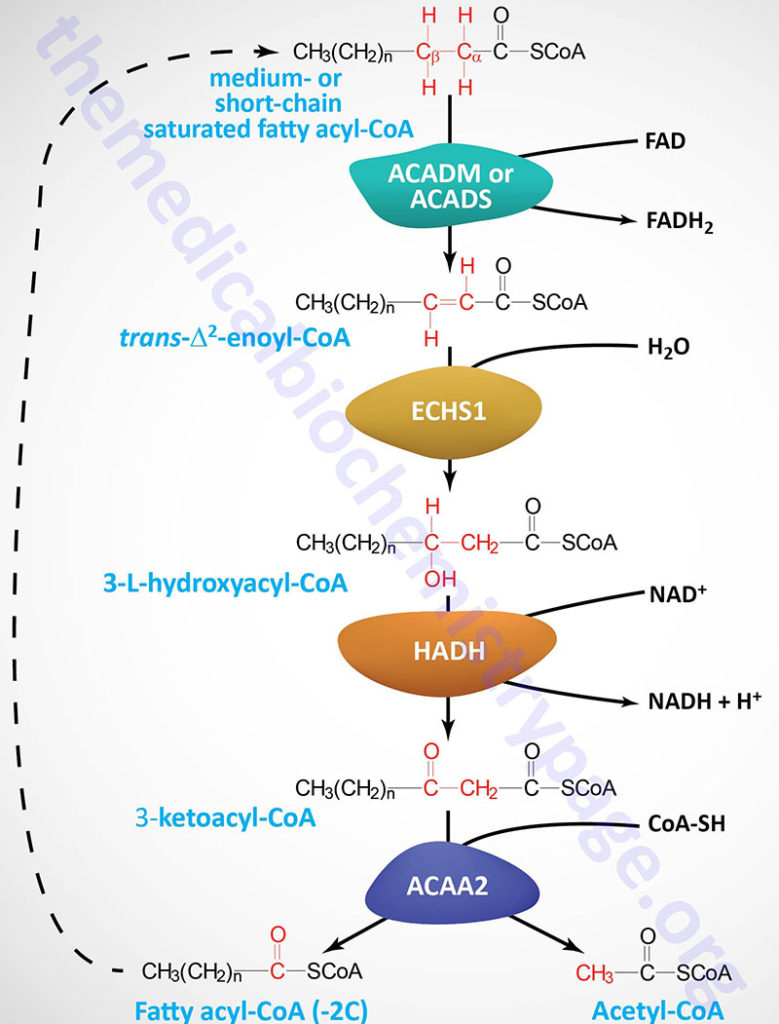
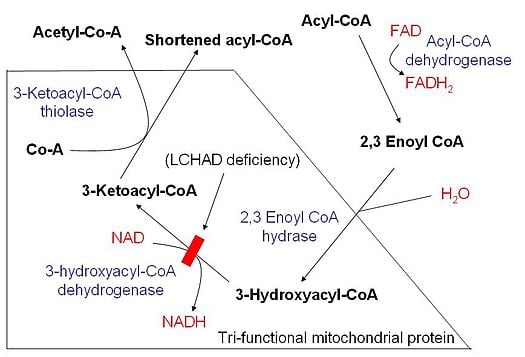
During beta-oxidation fatty acid molecules are broken down by removing two-carbon units from the carboxyl end of a fatty acid molecule to produce acetyl-CoA. Activation Transport proper beta-oxidation. FADH 2 NADH and H.
What are products of beta-oxidation. In biochemistry and metabolism beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA which enters the citric acid cycle and NADH and FADH2 which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport chain. Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids Fatty acid oxidation is the mitochondrial aerobic process of breaking down a fatty acid into acetyl-CoA units.
The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondria. Quantitative Human Physiology Second Edition 2017. Those that go to the electron transport chain immediately and those that need further processing.
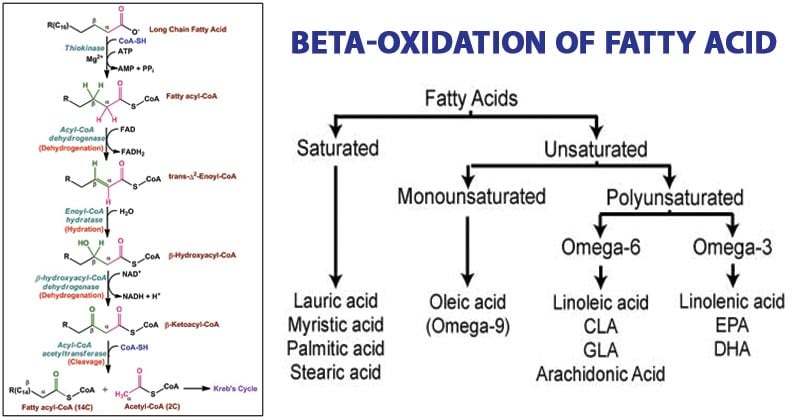
FADH 2 NADH and H. FAO also known as β-oxidation is the process of breaking down fatty acids into substrates utilized in mitochondrial ATP production. Acetyl CoA FADH 2 NADH and H The overall reaction using palmitoyl CoA 160 as a model substrate.
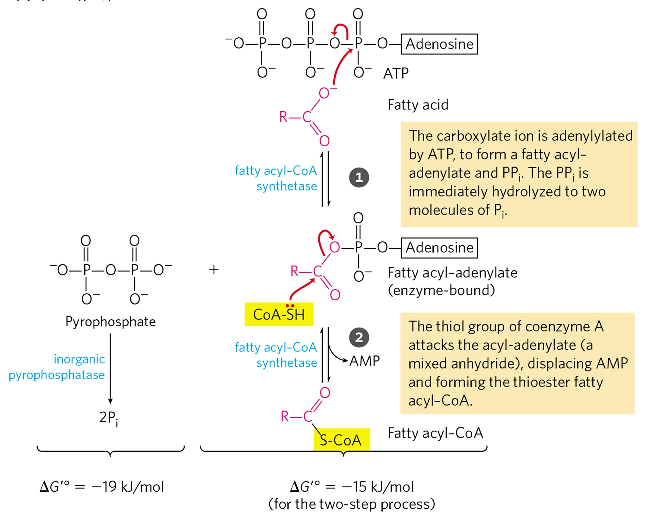
-Excess is stored as fat in adipose tissue. Fatty acids inside the cell are activated by long chain fatty acyl-CoA ligase which attaches coenzyme A CoA a. Activation of fatty acid is done in the cytosol cyt View the full answer.
In biochemistry and metabolism beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA which enters the citric acid cycle and NADH and FADH2 which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport. The products of beta-oxidation are. Beta-oxidation is the process by which long chain fatty acyl CoA is degraded.
The products of beta-oxidation are. The bond is broken between the second carbonbeta carbon and the third carbongamma carbon hence the name beta oxidation. Beta oxidation is a metabolic process involving multiple steps by which fatty acid molecules are broken down to produce energy.
In this form the fatty acids can be used by the body as fuel to generate adenosine triphosphate ATP through the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain ETC. Beta oxidation In biochemistry and metabolism beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down 1 in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA which enters the citric acid cycle and NADH and FADH 2 which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport chain. Beta-oxidation is a catabolic process where fatty acids are broken down to produce acetyl CoA.
6 11 Fatty Acid Oxidation Biology Libretexts
6 11 Fatty Acid Oxidation Biology Libretexts
Omega Oxidation W Oxidation Of Fatty Acid

Beta Oxidation Definition Steps And Quiz Biology Dictionary
Beta Oxidation Of Fatty Acid Online Science Notes

Fatty Acid Beta Oxidation Abcam

Fatty Acids Synthesis And Catabolism Take Place Simultaneously In Plant Download Scientific Diagram
Beta Oxidation Of Fatty Acid Online Science Notes
Beta Oxidation Of Fatty Acid Online Science Notes
What Is The Beta Oxidation Of Palmitic Acid Quora
What Is Meant By The Oxidation Of Fatty Acids Quora

What Would Be Formed On The Beta Oxidation Of A Fatty Acid With An Odd Number Of Carbon Atoms Quora

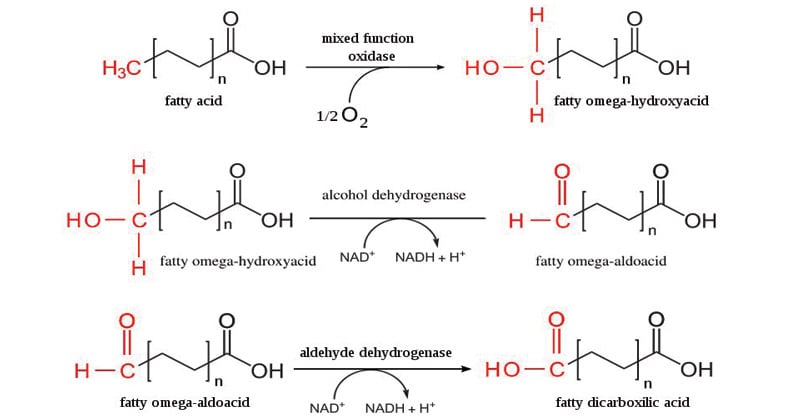
𝜶 Oxidation Of Fatty Acids Refsum S Disease W Oxidation

Oxidation Of Fatty Acids Via Beta Oxidation Biochemistry Notes Pharmaxchange Info

Fatty Acid Oxidation In Cell Fate Determination Trends In Biochemical Sciences
Lipolysis And The Oxidation Of Fatty Acids The Medical Biochemistry Page
Comments
Post a Comment